描述
basic design
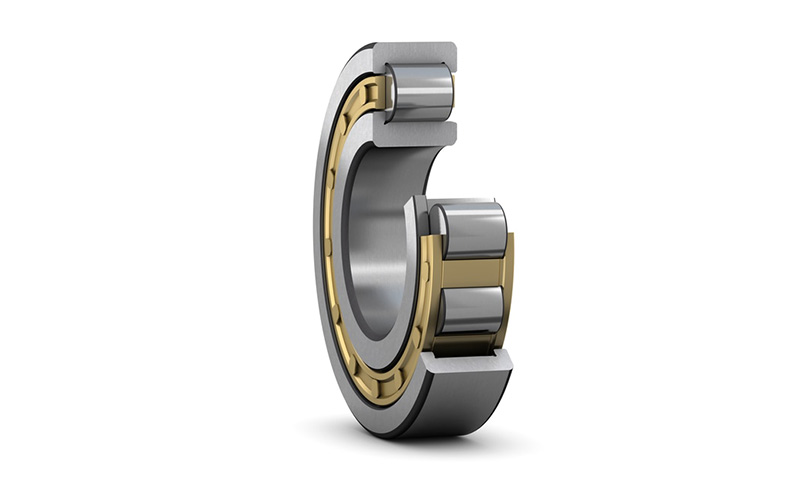
The most basic design of a single row cylindrical roller bearing is shown here.
NU type bearing (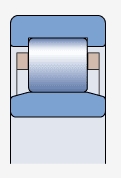 )
)
Both sides of the outer ring have integral blocking edges, while the inner ring has no blocking edges
Allow axial displacement of the shaft relative to the bearing seat in two directions
Can be used in conjunction with appropriate corner rings to achieve axial positioning of bearings (appropriate corner rings)
N-type bearing (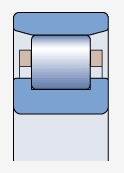 )
)
The inner ring has integral blocking edges on both sides, while the outer ring has no blocking edges
Allow axial displacement of the shaft relative to the bearing seat in two directions
NJ type bearing (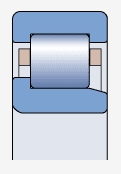 )
)
Both sides of the outer ring have integral blocking edges, while one side of the inner ring has blocking edges
Allow axial displacement of the shaft relative to the bearing seat in only one direction
Used for axial positioning in one direction
Can be used in conjunction with appropriate corner rings to achieve axial positioning of bearings in one direction (appropriate corner rings)
NUP type bearing (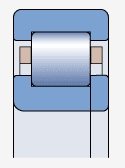 )
)
Both sides of the outer ring have integral blocking edges, one side of the inner ring has integral blocking edges, and the other side has movable blocking edges
Used for axial positioning in two directions
British bearings
The IMCB imperial bearing design (product table) of CRL and CRM series conforms to metric N-type 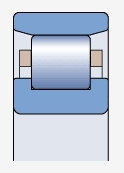 ). This type of bearing is mainly used in the aftermarket, so IMCB recommends not using these bearings for new bearing configuration designs.
). This type of bearing is mainly used in the aftermarket, so IMCB recommends not using these bearings for new bearing configuration designs.
Appropriate corner ring (thrust ring)
Used in conjunction with NU type bearings for axial positioning in one direction (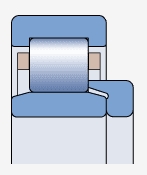 )
)
Corner rings should not be used on both sides of NU type bearings to avoid axial clamping force on the rollers.
Used together with NJ type bearings for axial positioning in two directions (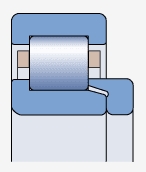 )
)
Made of carbon chromium bearing steel
After hardening and grinding processing
Has the maximum axial runout that meets the common tolerance level of bearings
Use the model series HJ along with the corresponding bearing size series and size representation
Please refer to the product table for the available models
Need to order separately
The reasons for designing corner rings in bearing configurations include:
There are no NJ or NUP type fixed end bearings in the product range
To provide an extended inner ring mating surface for bearings used as fixed ends when subjected to heavy loads:
Compared to NUP designed bearings with shorter inner rings and movable ribs, NJ type bearings equipped with HJ corner rings have an extended inner ring mating surface
Simplify design or installation procedures
Other designs
NUB type bearing (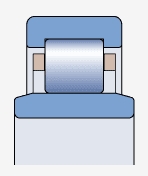 )
)
Both sides of the outer ring have integral blocking edges, while the elongated inner rings on both sides have no blocking edges
Allow axial displacement of the shaft relative to the bearing seat in two directions
NJP type bearing (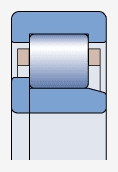 )
)
Both sides of the outer ring have integral blocking edges, and one side of the inner ring has a movable blocking edge
Used for axial positioning in one direction
NF type bearing (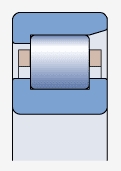 )
)
Both sides of the inner ring have integral blocking edges, and one side of the outer ring has integral blocking edges
Used for axial positioning in one direction
NP type bearing (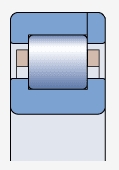 )
)
Both sides of the inner ring have integral blocking edges, one side of the outer ring has integral blocking edges, and the other side has movable blocking edges
Used for axial positioning in two directions
Other models
Bearings without inner or outer rings
Can be provided based on the following conditions:
NU type bearing without inner ring (RNU series,  )
)
In order to obtain a larger shaft diameter, thereby improving the strength and stiffness of the shaft
Provide tolerance limits for inner diameter Fw in accordance with DIN 5412-1 standard
Some of the available sizes are listed in the product table
N-type bearing without outer ring (RN series, 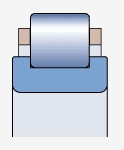 )
)
Axial displacement of the shaft relative to the bearing seat is allowed, but limited by the width of the raceway:
RNU bearings depend on the width of the raceway on the shaft
RN bearings depend on the width of the raceway on the bearing seat
The parts that are usually used as raceways on the shaft or in the bearing seat require quenching hardening and grinding processing (with the journal and bearing seat inner hole surfaces as raceways)
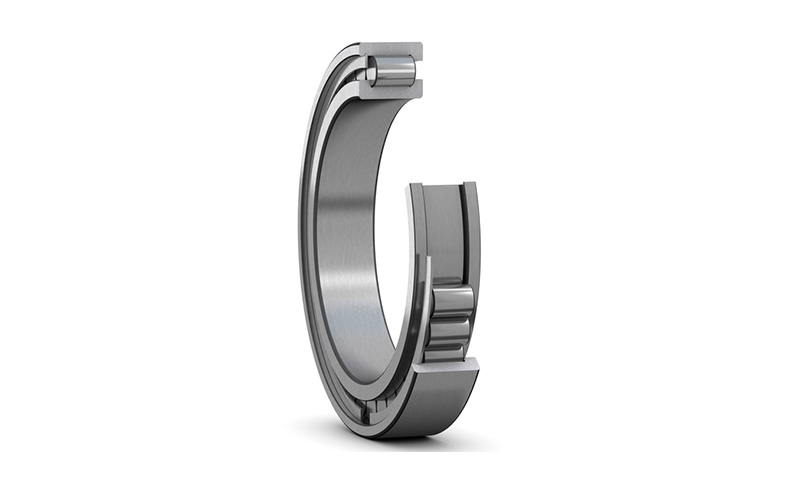
Bearings with tapered holes (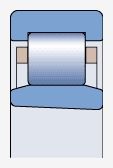 )
)
Can provide bearings with 1:12 tapered holes (model suffix K)
The radial clearance of the bearing is slightly larger than that of the corresponding cylindrical bore bearing
A bearing with a stop ring groove on the outer ring (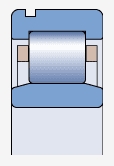 )
)
Represented by the suffix N of the model number
It can be axially positioned in the bearing seat through the stop ring:
Space saving
Shorten installation time
Bearing with outer ring with positioning groove (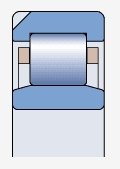 )
)
Can provide bearings with one or two positioning slots (model suffix N1 or N2)
The distance between two positioning slots is 180 °.
In bearing applications that require clearance fitting installation, it can prevent the outer ring from rotating
Paired bearings
When paired with bearings, the height difference of different cross-sections between each bearing must be controlled within a very small tolerance range
Tighter tolerance range control is a prerequisite for each bearing in the paired bearing to be able to withstand the same load.
The following pairing combinations are available:
Two bearings paired together (model suffix DR)
Three bearings paired together (model suffix TR)
Four bearings paired together (model suffix QR)





